How the new LLM Topic Assignment works (New AI)
Understand how AI assigns topics and refine results by improving topic descriptions.
🔎 In this article:
Key Improvements
- State-of-the-art AI model: Leverages project context (titles, descriptions, columns, question info) plus review content for highly accurate assignments.
- Less manual input required: High-quality results often after the first run.
- Topic descriptions matter: AI relies heavily on them, giving you more control.
- Longer texts supported: Now handles texts up to 20,000 characters (previous limit: 1,000).
- Multilingual support: Works across 100+ languages natively.
Best Practices (Before Running the Analysis)
Apply these steps before your first AI run to achieve the best results:
Project & Question Context
In addition to text + reviewed texts, the AI now uses the following fields during training:
-
Project Title
-
Project Description

-
Question Name
-
Question Description
Best Practices
-
Use descriptive titles instead of generic ones if available
Example: Use “Feedback on Delivery Process” instead of “Q3”. -
Add contextual info to descriptions:
-
Lesser-known companies or terms
Example: “XXX is a subsidiary of YYY that focuses on manufacturing.” -
Technical or company-specific terms
-
Define acronyms or jargon that might not be widely known.
-
Generally, the AI will be able to understand technical terms even if they are only known to specialists in the field. However, if the terms are uncommon acronyms or are company-specific, it may be useful to define them.
-
-
-
Sentiment guidance
Example: If responses are from complaints, say so, this helps the AI interpret tone or sarcasm better.
💡 Doing this upfront ensures that the AI will generate clearer and more accurate topic descriptions when you start the analysis.
Best Practices (When Starting Analysis)
Once you click Start Analysis, the system generates the first set of topic descriptions:
Topic descriptions are now a major input for the AI.
-
Review auto-generated descriptions → check if they make sense.
-
Refine unclear or ambiguous topics:
-
Reorganize or merge topics before confirming the first run.
-
If you want a fresh AI-written description: delete the old one → it will regenerate on the next run.
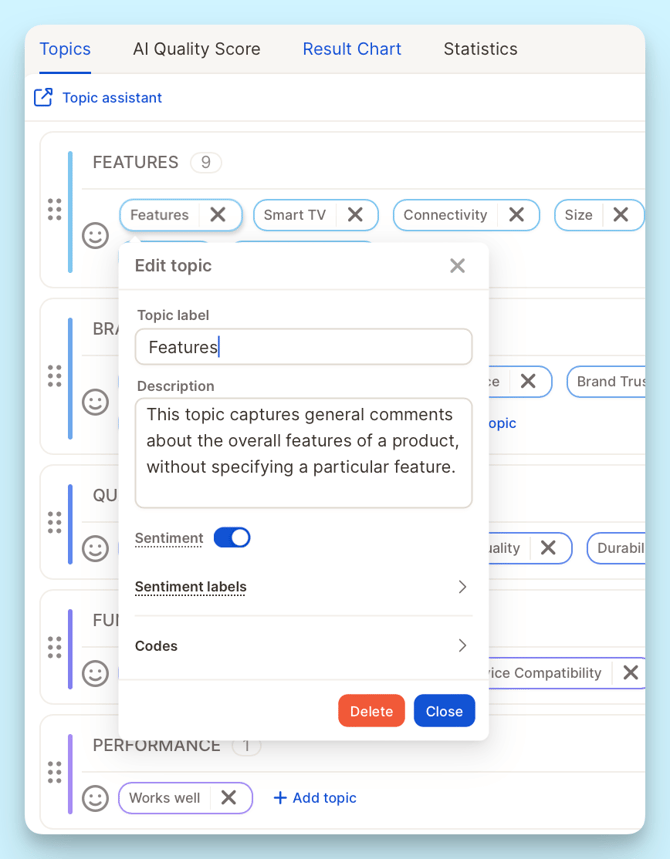
Notes on Behavior
-
Descriptions apply to the next training round (not instantly)
-
Changing a topic label does not auto-update the description. Usually, this is not an issue if it is still referring to the same topic, but if you change it to something very different, you will have an outdated and irrelevant description.
Workflow Overview
1. Enable and Start Analysis
-
Click Enable AI.
-
Review the generated topic descriptions immediately.
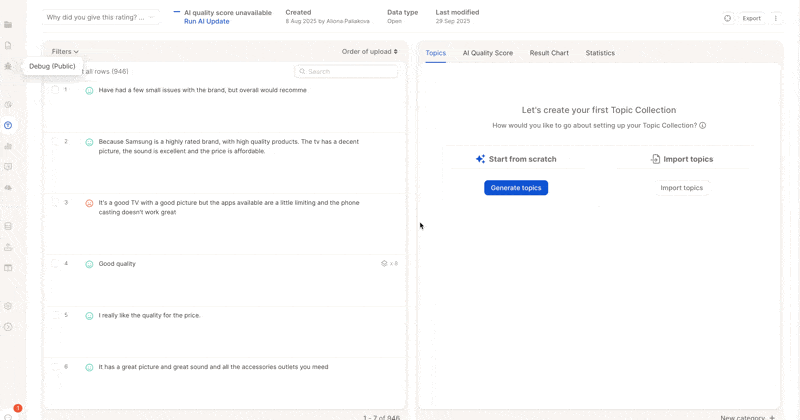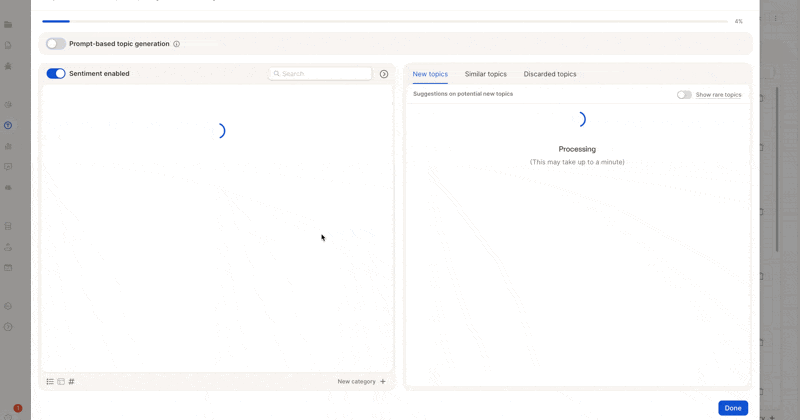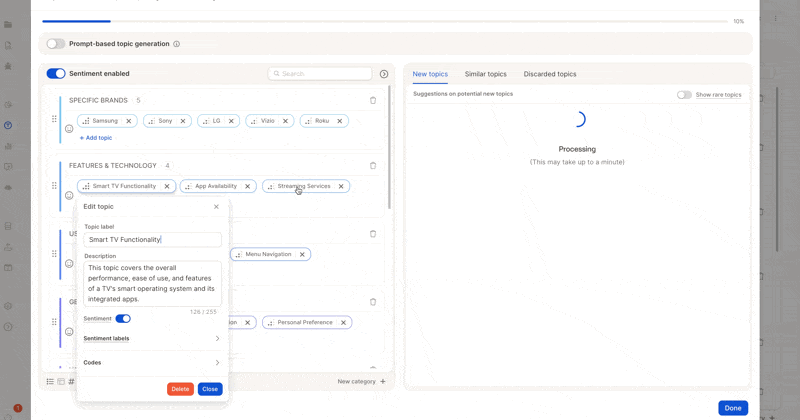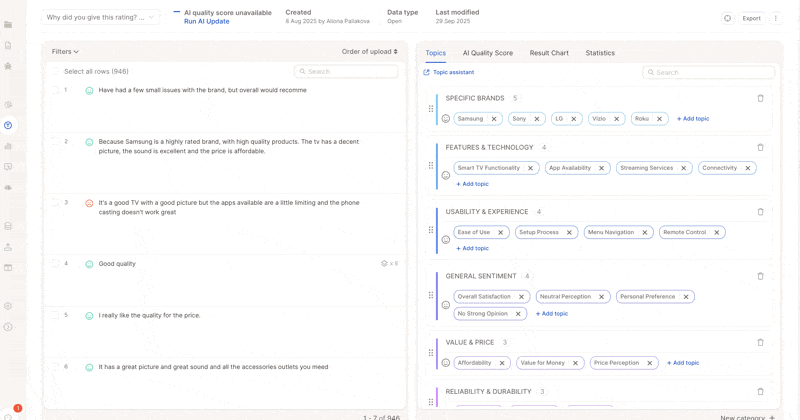
2. Refine Topics & Descriptions
-
Merge or reorganize topics.
-
Adjust descriptions to better match your intent.
3. Run the AI
-
Hit Done → triggers the first run.
-
Duration: seconds to minutes depending on dataset size.
-
Expect human-level accuracy even without manual reviews.
4. Review Results
-
Check the overall score and the % of rows without topics.
-
Make adjustments: merge similar topics, refine descriptions, add missing ones.
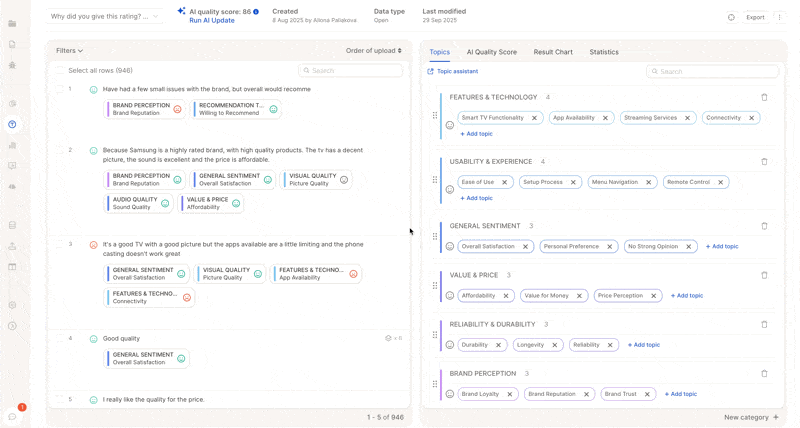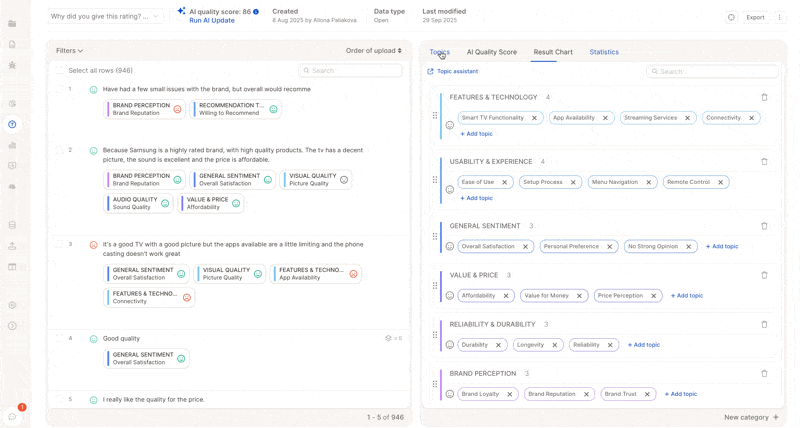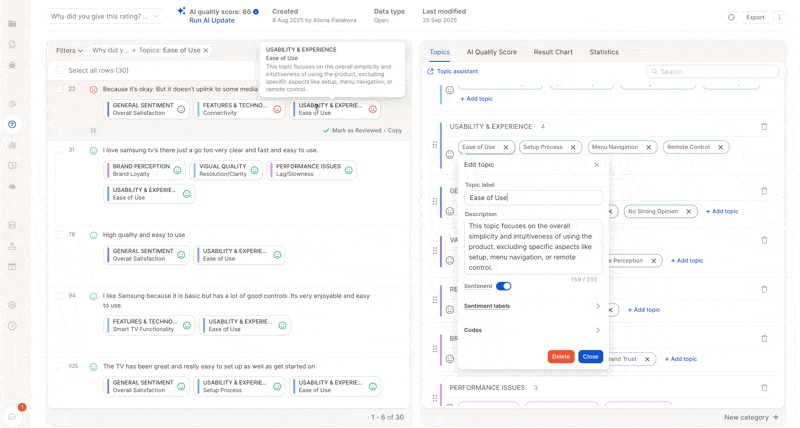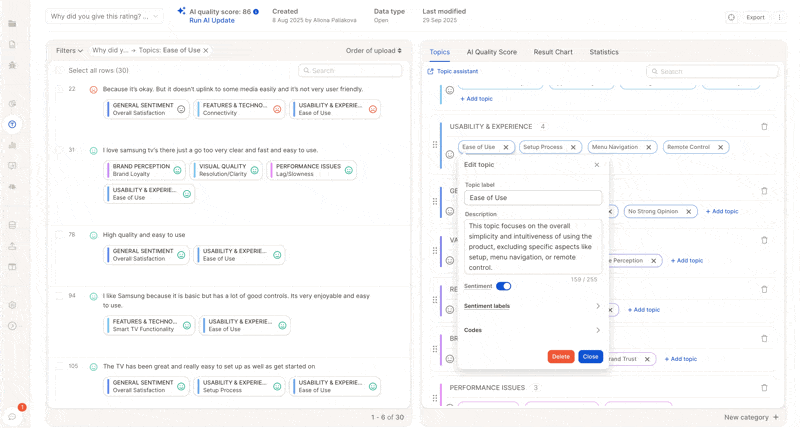
5. Trigger Updates: Full vs. Partial Runs
Caplena gives you full control over when and how AI updates are triggered, they are no longer automatic.
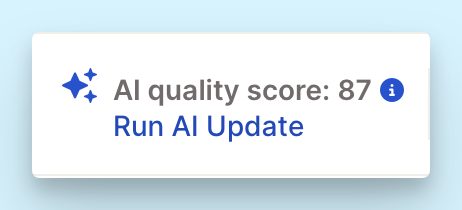
You can choose between two types of updates. Caplena automatically detects whether a partial or full AI update is needed based on your changes, and suggests the best option. In 95% of cases, the suggested type is the correct one. You’ll still have full control and can override the suggestion if needed.
Partial AI Update (New!)
Caplena now supports partial updates, saving time and AI usage when only small changes are made.
Use this when you:
-
Add a new topic
-
Edit the description of an existing topic
What happens:
-
Only the affected rows are reprocessed
-
Faster and more efficient than full re-runs
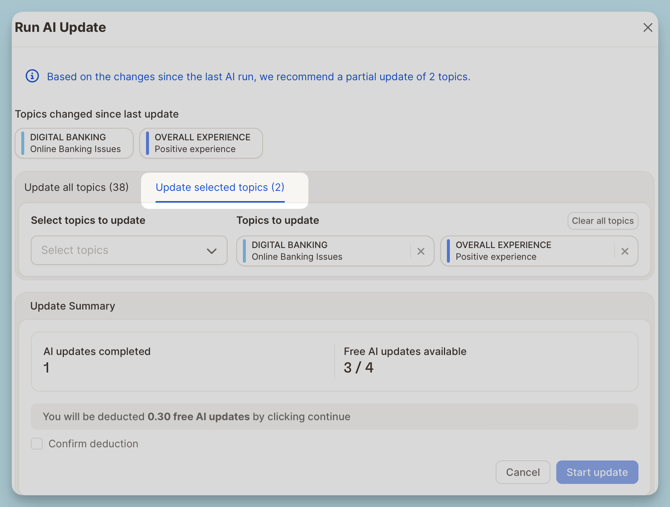
In the screenshot above, only 2 topics were changed. We recommend a partial update of just those topics, costing only a fraction of a full update.
Full AI Update
A full update is recommended when you’ve made multiple or broader changes, such as:
-
Adding or editing many topics at once
-
Significantly reworking the topic structure or descriptions
Why run a full update?
-
Ensures consistency across the entire dataset
-
Often more cost-efficient than running many partial updates separately
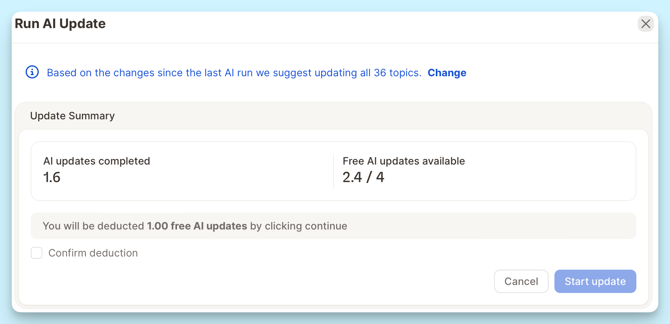
- The number of included AI runs may vary depending on your Caplena plan.
- The extra AI run cost is 50% of the original import. For example, if the first import of a column used 1,000 credits, then each additional run would cost 500 credits.
Manual Reviewing Tips
It is still possible and useful to manually review rows! However, we expect that the new AI should have a solid enough baseline to reduce the amount of manual reviewing required.
Where to Focus Your Time:
- Update the descriptions and make topics clearer instead of reviewing many individual examples
- If reviewing is necessary or you prefer it over editing descriptions:
- Skip easy/obvious rows, the AI got it right
- Focus on borderline or complex examples
Label fewer rows, but make them count.
(The AI now benefits more from quality over quantity.)
Supported languages:
The new AI supports more languages natively
- Afrikaans (af)
- Albanian (sq)
- Amharic (am)
- Arabic (ar)
- Armenian (hy)
- Assamese (as)
- Azerbaijani (az)
- Basque (eu)
- Belarusian (be)
- Bengali (bn)
- Bosnian (bs)
- Bulgarian (bg)
- Catalan (ca)
- Cebuano (ceb)
- Chinese (Simplified and Traditional) (zh)
- Corsican (co)
- Croatian (hr)
- Czech (cs)
- Danish (da)
- Dhivehi (dv)
- Dutch (nl)
- English (en)
- Esperanto (eo)
- Estonian (et)
- Filipino (Tagalog) (fil)
- Finnish (fi)
- French (fr)
- Frisian (fy)
- Galician (gl)
- Georgian (ka)
- German (de)
- Greek (el)
- Gujarati (gu)
- Haitian Creole (ht)
- Hausa (ha)
- Hawaiian (haw)
- Hebrew (iw)
- Hindi (hi)
- Hmong (hmn)
- Hungarian (hu)
- Icelandic (is)
- Igbo (ig)
- Indonesian (id)
- Irish (ga)
- Italian (it)
- Japanese (ja)
- Javanese (jv)
- Kannada (kn)
- Kazakh (kk)
- Khmer (km)
- Korean (ko)
- Krio (kri)
- Kurdish (ku)
- Kyrgyz (ky)
- Lao (lo)
- Latin (la)
- Latvian (lv)
- Lithuanian (lt)
- Luxembourgish (lb)
- Macedonian (mk)
- Malagasy (mg)
- Malay (ms)
- Malayalam (ml)
- Maltese (mt)
- Maori (mi)
- Marathi (mr)
- Meiteilon (Manipuri) (mni-Mtei)
- Mongolian (mn)
- Myanmar (Burmese) (my)
- Nepali (ne)
- Norwegian (no)
- Nyanja (Chichewa) (ny)
- Odia (Oriya) (or)
- Pashto (ps)
- Persian (fa)
- Polish (pl)
- Portuguese (pt)
- Punjabi (pa)
- Romanian (ro)
- Russian (ru)
- Samoan (sm)
- Scots Gaelic (gd)
- Serbian (sr)
- Sesotho (st)
- Shona (sn)
- Sindhi (sd)
- Sinhala (Sinhalese) (si)
- Slovak (sk)
- Slovenian (sl)
- Somali (so)
- Spanish (es)
- Sundanese (su)
- Swahili (sw)
- Swedish (sv)
- Tajik (tg)
- Tamil (ta)
- Telugu (te)
- Thai (th)
- Turkish (tr)
- Ukrainian (uk)
- Urdu (ur)
- Uyghur (ug)
- Uzbek (uz)
- Vietnamese (vi)
- Welsh (cy)
- Xhosa (xh)
- Yiddish (yi)
- Yoruba (yo)
- Zulu (zu)
